Class 12 Self Management Skills Notes | Quick Revision for CBSE Boards

Session 1: Self Mangement
What is Self-Management
- Self-management (Self-control) is the ability to regulate emotions, thoughts, and behaviour effectively in different situations.
- Self-management helps improve essential skills such as:
- Being on time
- Stay discipline
- Solving problems
- Working in organized manner.
- Students with strong self-management are punctual, disciplined, focused, and respectful.
Ways to improve self-management | Core Aspects of Self-Management
- Positive Thinking → Believing in ability to get things done and be happy.
- Result Orientation → Aim high and stay focused to get desired results.
- Self-awareness → Be aware of one’s strengths/weaknesses, and make the best use of strengths.

Session 2: Motivation and Positive Attitude
Motivation
- Motivation comes from the word ‘motive’, which means the driving force that directs our actions towards a goal.
- It is a mental attitude based on belief and hope which help us achieve our dreams and stay focussed on success.
Types of Motivation:
- Intrinsic Motivation: When motivation comes from within to do something without expecting any reward is called Intrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation makes people engage in activities because they enjoy them, feel satisfied, or find personal happiness.
- Extrinsic Motivation: When motivation comes from external rewards such as money, recognition, incentives is called extrinsic motivation. Extrinsic motivation drives people to engage in activities to gain respect, recognition and appreciation.
- Class 12 Self Management Skills Notes
Class 12 Self Management Skills Notes
Positive Attitude
- Positive attitude leads to happiness, make better decisions, maintain stronger relationships, and success.
- Positive attitude Improves mental and physical health.
- Positive attitude helps people handle challenges better and move forward more easily unlike negative attitude.
How to maintain a Positive Attitude | Ways to maintain positive attitude
- Start the day with a routine that includes affirmations, smiling, and listing tasks to accomplish.
- Feed your mind with positivity by reading motivating books, listening to uplifting music, and watching inspiring movies.
- Be proactive → control how you feel despite circumstances.
- Focus on solutions, not problems.
- Learn from failures and keep working towards the goal.
- Be cheerful and keep working hard to achieve dreams.
Long-term techniques to maintain positive attitude:
- Physical Exercise & Fresh Air: Do Yoga, meditation, outdoor play.
- Healthy Diet: Eat Balanced food for strength and efficiency.
- Organise Academic Life: Keep Notes, complete assignments, track deadlines.
- Adequate Sleep: 7 hours minimum sleep for recharge of mind and body.
- Holidays & Breaks: Spend time with family/friends to refresh.
Value of Positive Attitude in Student Life
- Helps in exams → accept results, keep working harder.
- Job interviews → even if rejected, stay persistent and positive.
- Essential for success in all aspects of life.
Session 3: Stress Management
What is Stress?
Stress is state of feeling upset, hopeless, or unable to achieve goals. It may affect both mental and physical health. Stress can be managed with self-control and positive attitude.
Ways to Manage Stress:
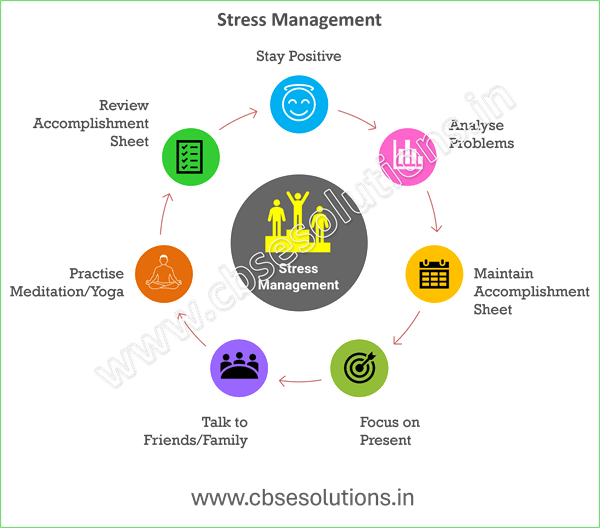
Class 12 Self Management Skills Notes
Session 4: Result Orientation
- Result Orientation is the ability to recognise important results and focus on the steps required to achieve them. It Focuses on outcomes of task rather than the process.
- An ideal individual is proactive, goal-driven, and takes necessary steps to achieve targets.
How to Become Result-Oriented
- Set Clear Goals – First step towards meeting targets.
- Prepare an Action Plan – Gives details of actions/steps/changes to be taken to achieve target. Each action/step/change include following information:
- What changes will occur?
- Who will carry them out?
- When changes will take place?
- How long will the change stay?
- What resources are needed?
- Who to communicate with and what to share?
- Use the Right Resources/Tools – Ensure availability of books, materials, or guidance.
- Communicate with Mentors & Peers – Seek help from mentors/peers in setting realistic goals.
- Make a Calendar – Monitor progress regularly.
- Work Hard – Believe in dreams and keep working hard.
Goal Setting
- Goal Setting helps to identify what we want, how to achieve it, and how to measure success.
- Goal setting should be clear, easily understood, with a defined purpose and objective.
How to set a goal?
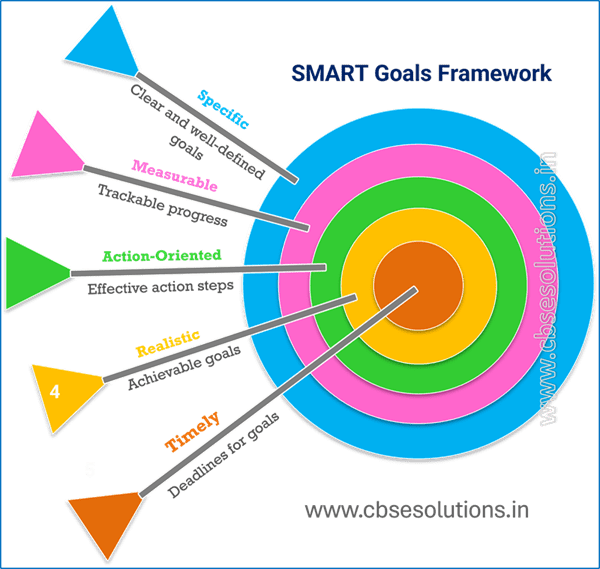
we can use SMART model for setting our goals.
SMART Goals
Examples of Result-Oriented Goals
- A student sets a goal of scoring high marks.
- An athlete runs 5 miles daily.
- A traveller plans to reach a city in 3 hours.
Class 12 Self Management Skills Notes
Session 5: Self-Awareness
- Self-awareness refers to understanding one’s needs, desires, habits, traits, behaviours, and feelings.
- Lack of self-awareness leads to confusion and unclear direction.
- Helps in understanding oneself, others, and the world objectively.
Steps Towards Self-Awareness
- Be aware of emotions.
- Track and record feelings.
- Expand awareness to different areas of life.
Personality and Personality Traits
- Personality → Cluster of thoughts, feelings, and behaviours that make a person unique.
- Personality traits → Long-lasting patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviour that distinguish individuals.
- Personality develops through temperament, character, environment, and culture.
Five Factor Model (FFM) | The Big Five Personality Traits
- Openness – Individual with openness is creative, curious, adventurous.
- Conscientiousness – Individual with Conscientiousness is disciplined, responsible, caring.
- Extraversion – Individual with Extraversion is outgoing, talkative, confident.
- Agreeableness – Individual with Agreeableness is Kind, cooperative, sympathetic, warm and considerate.
- Neuroticism – Individual with Neuroticism are anxious, insecure, prone to negative emotions.
Common Personality Disorders
Cluster A: Suspicious
People falling under this cluster always mistrust others and are suspicious, even when there is no need to do so.
- Paranoid Personality Disorder → Distrust for others, holding grudges against others.
- Schizoid Personality Disorder → Person is detached, aloof, and prone to interoception, avoids relationships.
- Schizotypal Personality Disorder → Odd beliefs, misinterprets behaviours, avoids intimate relationships.
Cluster B: Emotional & Impulsive
- Antisocial Personality Disorder → Ignores social rules, aggressive, impulsive, and irritating.
- Borderline Personality Disorder → Emotional instability, low self-worth, violent and impulsive, self-harm tendencies.
- Histrionic Personality Disorder → Overly dramatic, attention-seeking, can be easily influenced by others.
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder → Sense of self-importance, lack of empathy for others.
Cluster C: Anxious
- Avoidant Personality Disorder → socially inept, unappealing or inferior, and constantly fear being embarrassed, criticised or rejected.
- Dependent Personality Disorder → Lacks self-confidence, heavily dependent on others for their needs.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder → Excessive concern with orderliness, perfectionism and attention to details.
Steps to Overcome Personality Disorders
- Talk to someone and share feelings.
- Maintain healthy body.
- Build self-confidence.
- Engage in hobbies (music, dance, painting).
- Stay positive by choosing words like ‘challenges’ instead of ‘problems’